Outsourced Tax Planning & Preparation Packages

For the sophisticated individual taxpayer:
Designed for high-net-worth individuals, business owners, and those with varied income sources, this package ensures clarity and strategy in managing diverse and complex tax landscapes.
Starting from
$149
per month

Tailored for small to medium-sized businesses:
This package offers precise and expert solutions for SMBs. We pinpoint and tackle unique business tax challenges, providing insights to refine and streamline your tax obligations.
Starting from
$215
per month
Corporate Tax Estimate
Add-on Customized Services:
For the ultimate flexibility and customization, our Customized Services are available to cater to your specific needs, whether one-time or periodic. These services are perfect for unique tasks, consultations, or when you need expert assistance on an as-needed basis.
Billing Structure: Retainer pricing for these projects will be determined separately. These services may be required on a one-time or periodic basis.
Transparent Flexibility: Use our services as little or as much as you need without being locked into a fixed price.
Tailored Solutions: Whether it’s a quick consultation or a longer-term project, you’re in control of the services you receive.
- Prior Year Past due Income Tax Return Filings
- Accounting/Bookkeeping Cleanup Projects
- Foreign/International filings (FinCen, FBAR, 5471, 5472 filings)
- Multi-State Expansion and Tax Filing Compliance
- Implementing Stock Options & Equity Compensation Plans
- Mergers & Acquisitions and Reorganization Tax Planning
- Shareholder/Partner Expansion
- IRS Audit Representation
- Government Notice Support – for tax returns completed by other firms
- Alternative Investment Tax Strategies (e.g.hedge funds, private equity, real estate)
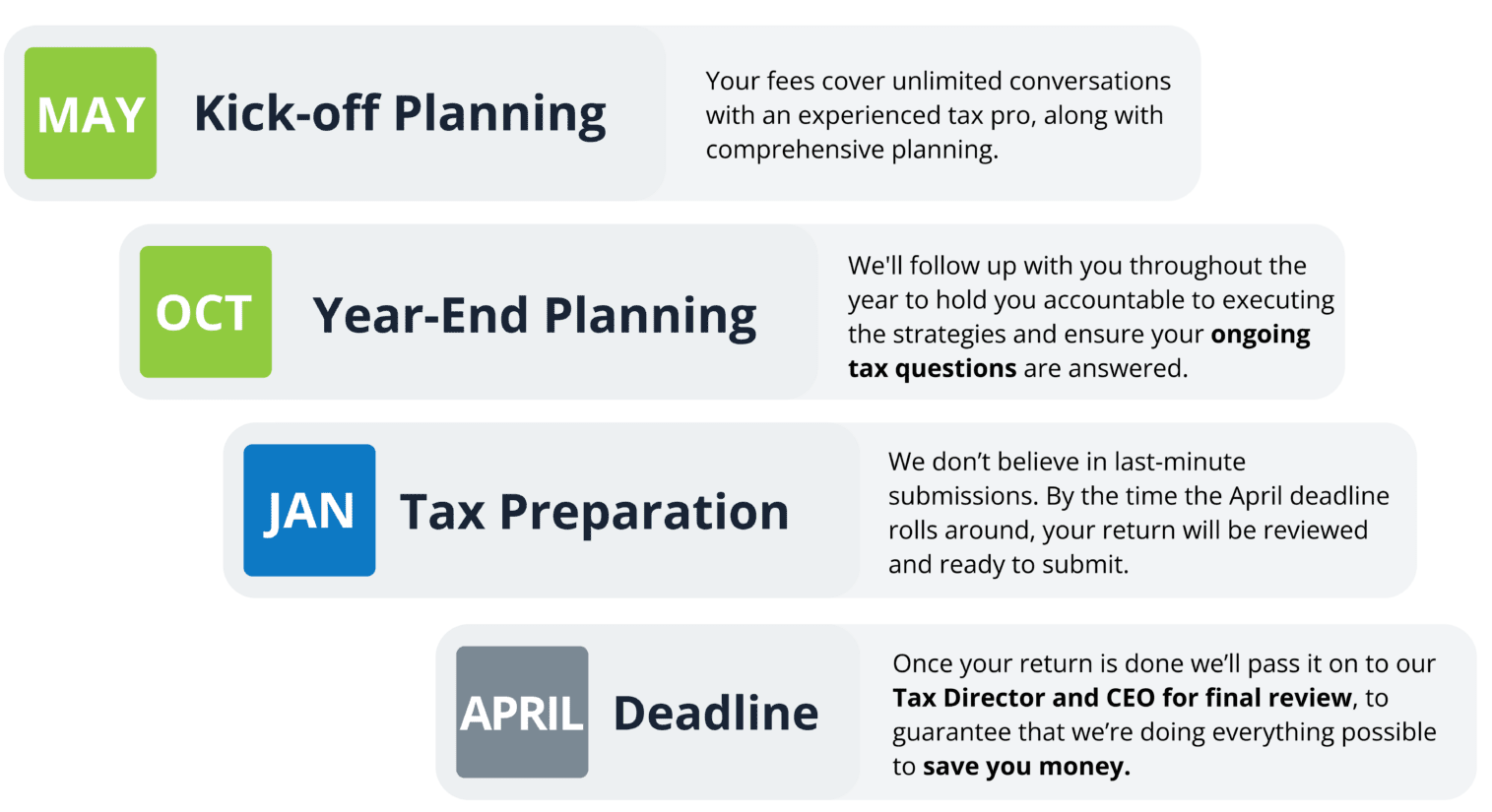
Tax Planning Life Cycle
We guarantee at least two tax planning sessions a year, including year-end planning, before preparing your return in January.
If you’re still not convinced we’re right for you, we have an easy exit plan, and you can cancel at any time.
Discover Our Simplified Onboarding Process
Tax Subscription FAQs
What does my Tax Subscription Fee include?
- Income tax return preparation & tax return review
- Income tax filing (electronic or paper)
- Extension filings (US firms)
- Estimated quarterly taxes (US firms)
- Tax questions
- Tax projections
- Tax strategy optimization calls
- IRS notice and correspondence support
- Premium tax content access
Can I opt out and still do hourly pricing?
Our objective is to ensure that all clients are integrated into a single, unified billing system for optimal efficiency and consistency. However, we have identified some clients for whom continuing with hourly billing is more practical, particularly those experiencing significant fluctuations in activity year over year. If you feel this applies to your situation, we encourage you to reach out to us for a discussion.
What is considered a customized Tax Service “Add-on”?
- Prior year past due income tax return filings
- Accounting/bookkeeping cleanup projects
- Foreign/International filings (FinCen, FBAR, 5471, 5472 filings)
- Multi-state expansion and tax filing compliance
- Implementing stock options & equity compensation plans
- Mergers & acquisitions and reorganization tax planning
- Shareholder/Partner expansion
- IRS Audit representation
- Alternative investment tax strategies (e.g., hedge funds, private equity, real estate).
What is not included in the Tax Subscription?
- Payroll tax filings
- Sales tax filings
- Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) reporting
Is it possible to Cancel my Subscription at any time?
We require a 30-day notice of cancellation for all pricing plans.If the cancellation occurs before the term concludes (term: Jan – Dec), you will not be eligible for our tax return preparation services.
Instead of paying the 2024 Monthly fee, can I Prepay it all at once similar to how I pay my insurance premiums?
Yes, we can set that up as well. You will just need to email us this request and we can set up the billing system accordingly.
Need assistance with your tax?
Our CPAs Answer Your Tax FAQs
Our CPAs Answer Your Tax FAQs
I Need Help with My Taxes - Where Do I start?
Ideally, you want an experienced CPA for tax assistance, as automated services aren’t going to offer the thorough tax planning and preparation that a CPA can. At Fusion CPA we have outsourced, online accountants that are extremely dedicated to what they do.
We use accounting software to streamline your taxes, but we aren’t tied to any specific platforms and offer software integration too. This is valuable when your financial data is spread across a variety of platforms. Because we offer outsourced tax services, you only pay for the help you need!
You can contact one of our client success team to discuss your needs with a real person! If it looks like Fusion CPA is a good fit for you, we will put together a quote. Once you’ve accepted it, we will connect you with one of our expert CPAs.
When is Tax Season?
Individuals
For individual taxpayers, the tax year is the same as the calendar year, which means that it starts on January 1 and culminates on December 31. Business entities can follow the fiscal year or the calendar year. The question “when is tax season?” typically refers to the period in which tax returns can be sent to the IRS.
Tax filing season for the previous year starts on January 1 and ends with the regular filing deadline of April 15. If happened to be running behind and you had to file an extension then your tax filing is due by October 15.
Businesses
Business tax returns are due on March 15 for partnerships, and S-corporations. In the case of C-corporations, the deadline is on April 15 if they operate under the calendar year.
Read our extensive blogs as well as some end-of-year tax tips from our CPAs.
Limited liability and sole proprietors
Single member limited liability companies taxes are typically filed with the business owner’s personal tax return so the filing deadline is April 15th, and if an extension had to be filed then the tax filing is due by October 15th.
Where Do I View My Tax Refund?
Our clients can get in touch with our office after their tax returns are submitted in order to learn about the status of their refunds.
Where’s my refund if I filed my return already?
Alternatively, you can also check the federal government’s website set up for this purpose.
I Want to Know How Tax is Calculated
Individuals
It would take several pages to explain the basics of how tax is calculated in the United States because of the great diversity of taxpayers and their different financial situations. What you should know is that American taxation is progressive, which means that tax assessment levels will increase along with the income you report. Marginal and effective tax rates at the federal level have a lot to do with how tax is calculated; they range between 10% and 37% as of 2021, and they are by no means among the highest in the world.
If we were to boil down tax calculations to a single paragraph it would be as follows:
The most applicable filing status must be ascertained first; this is followed by a determination of all income sources and qualified deductions. These steps result in the calculation of taxable income, but there will be additional workflows to figure out if the overall tax liability can be lowered by means of credits such as education, healthcare, and child care in the case of individual tax returns.
Businesses
Tax rates are currently 21% on taxable income for US C Corporations, whereas S Corporations and Partnerships remain “flow through” entities and are not subject to Federal tax.
The process is different for business entities because of matters related to equipment, depreciation, payroll, and quite a few others; nonetheless, the common denominator crucial to tax calculation will always be the determination of taxable income. You can read our article explaining US corporate tax rates.
How Do I Choose the Right Entity?
There are several entity structures that businesses can choose from. Each structure comes with its advantages and drawbacks. The entity type that would work best for your business depends on different factors such as the size of your organization, your preferred tax structure, and more. A small business accountant can help you choose the structure that will suit your needs best. This article will explore the most suitable entity structure for your business.
How do I report income from self-employment or freelance work?
You report self-employment or freelance income on Schedule C of your tax return. If you use part of your home exclusively for your work or business, then you may be eligible for home office tax deductions. Self employed individuals can also benefit from other tax deductions, but must keep detailed records of qualifying expenses to be able to do so.
What is the difference between a tax deduction and a tax credit?
Tax deductions and tax credits are similar in that they both translate to more money in your pocket. The only difference is that the one saves you money by reducing your taxable income and the other does so by reducing your tax liability. Let’s take a closer look:
An individual or business can subtract tax deductible expenses – typically those seen as necessary for the business or individual earnings. This helps to reduce the amount of income subject to taxation and is considered a tax deduction. Tax credits on the other hand are designed to incentivize specific behaviors or activities that the government deems beneficial to individuals, businesses, or society as a whole. Examples of tax credits include those for education expenses or renewable energy technologies. These provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax liability.
What are estimated taxes and who needs to pay them?
Estimated taxes are periodic, estimated tax payments that must be made by individuals who receive income that are not subject to withholding. This includes self-employed individuals, freelancers, and those with significant investment income. Essentially, it is to pay the IRS an estimated amount of taxes based on the income received over a period. Use Form 1040-ES to calculate and submit your estimated tax payments and consult your CPA to ensure accurate submissions.
How do I handle taxes on investment income or capital gains?
Capital gains tax is typically payable on the profits made from selling an asset and is often in addition to corporate income taxes. Investment income and capital gains are reported on Schedule D of Form 1040. The tax rate depends on factors such as your income and how long you held the investment. For example: The tax rate on most net capital gain is no higher than 15% for most individuals. However, some or all net capital gain may be taxed at 0% depending on various factors. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional for personalized advice in this regard.
What are the implications of buying or selling a home on my taxes?
One of the primary tax benefits of homeownership is the mortgage interest deduction. You can deduct the interest paid on your mortgage loan from your taxable income. Selling a home on the other hand, could lead to capital gains taxes if your gains exceed the exclusion limits. There are potential tax benefits and implications for both scenarios. Consult with a tax advisor for guidance.
How does retirement income or contributions affect my taxes?
Traditional IRAs are tax-deferred, meaning that you don’t have to pay tax on any interest until you withdraw the money. Then, they are taxed at your ordinary income rate. The contributions you make to the account, however, may entitle you to a tax deduction each year.But, the tax treatment may vary based on the type of retirement account you have. It is advisable to consult with a trusted expert to avoid common tax mistakes for retirees.
How do I handle taxes if I've moved states during the year?
Moving to a new state can be intricate to navigate from a tax perspective. This is because different states have different tax rates and rules. You may need to file part-year resident returns in both states, which can be challenging to navigate if you are not familiar with tax residency rules per state. Consult your CPA to ensure compliance with state-specific tax laws.
What are the tax implications of owning or selling stocks and bonds?
Profits from selling stocks or bonds are subject to capital gains tax. The taxable part of a gain from selling section 1202 qualified small business stock is taxed at a maximum 28% rate. But, the tax rate depends on factors such as your income and how long you held the investment. Consult with a tax expert to have a look at your stock portfolio for personalized tax advice.
How do I report rental income and expenses?
Rental income and expenses are reported on Schedule E. You may be able to deduct rental-related expenses, including repairs and maintenance, to maximize deductions. But, it is crucial to keep detailed records of these expenses as evidence.Consult with a tax expert for personalized tax advice.
Can I claim a deduction for charitable donations?
Charitable donations are deductible and must be claimed as itemized deductions on Schedule A of Form 1040. For tax years 2023 and 2024, the limit on charitable cash contributions is 60% of your gross income. For compliance, if your charitable contributions meet certain criteria you must keep records to claim them as deductions on your tax return.
Are there government incentives or tax credits for buying an electric vehicle (EV)?
You may qualify for a credit up to $7,500 under Internal Revenue Code Section 30D if you buy a new, qualified plug-in EV or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCV). The credit is available to individuals and their businesses, but is subject to certain qualifying criteria.

The Fusion team were absolute rockstars with my tax cleanup for this year and last. They saved me thousands in mistakes that "the other guy" was making in my financial organization. They probably should have charged me more but it's too late, I already paid the invoice 😂But seriously, thank you all for your expediency and time this season and I look forward to working with you in 2024.You've gained a new customer for life!

Trevor and his team are the best! As a first time small business owner they took the time to answer my many questions, never making me feel like a nuisance, and always with a quick response. Very knowledgeable and always looking out for the best interest of their clients. Looking forward to many more years of work together thanks Fusion CPA!

I have never used a professional tax preparation service before, but I had a very complicated tax issue this year and Trevor and Steven were awesome in helping me resolve it.They were always accessible via email and phone and they took the time to break down complex tax provisions in a way that was easy to understand. I also appreciated how transparent they were about their fees and how efficient they were in researching issues and preparing my tax returns.
*The pricing structure displayed may change depending on the specific needs of your business. Please note that accurate and timely tax filing submissions and services require relevant and timely financial information to be provided to our CPAs, per the agreed and structured deadline schedule provided to our clients.